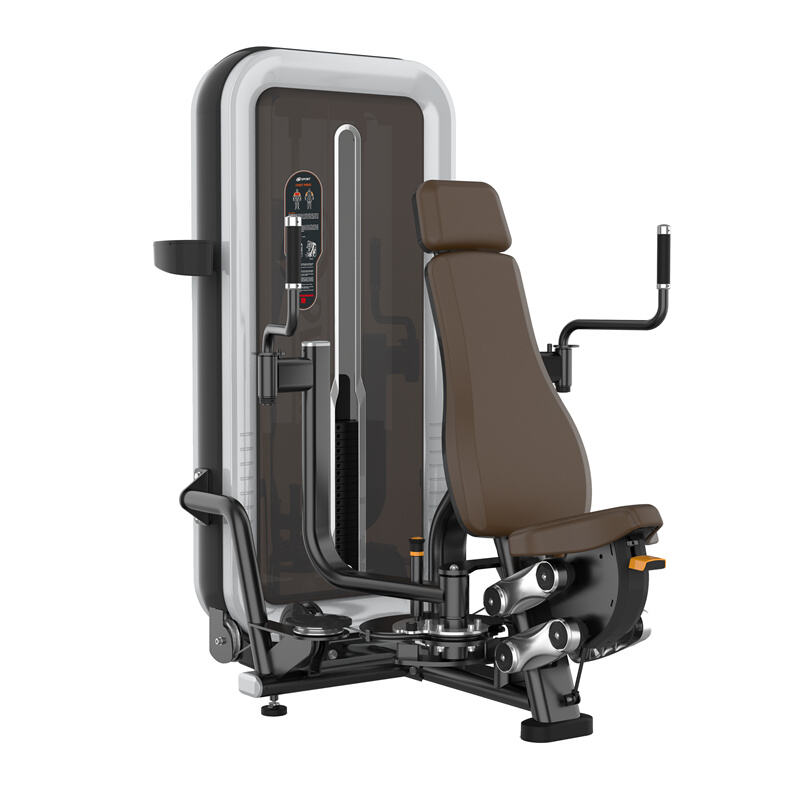
Understanding the Butterfly Machine: Design and Primary Function
What is the Butterfly Machine designed to target?
The butterfly machine works by focusing on those chest muscles, particularly the ones along the sternum area. What makes it different from lifting weights is that the arms follow a set path during the movement. This helps take some pressure off the shoulders while keeping the pecs working hard throughout the exercise, which is pretty important if someone wants to build defined chest muscles and overall strength. According to recent studies published in the Journal of Strength Training back in 2023, these kinds of fixed movement machines actually cut down on unwanted body movements by around 32 percent when compared with traditional weight training methods.
Key components enabling chest isolation
Three design elements ensure targeted muscle engagement:
| Component | Function | Impact on Chest Isolation |
|---|---|---|
| Angled handlebars | Maintain 15-20° elbow flexion to reduce triceps involvement | Focuses force on pecs |
| Adjustable seat | Positions shoulders parallel to moving arms | Prevents anterior delt dominance |
| Padded chest rests | Stabilizes torso while allowing full range of motion | Eliminates momentum transfer |
This biomechanical setup allows users to move 23% heavier loads with 40% less shoulder activation compared to dumbbell flys (Sports Medicine Quarterly, 2024), making it ideal for bodybuilders prioritizing chest development.
Mastering Proper Form and Technique on the Butterfly Machine
Step-by-Step Guide to Correct Posture, Grip, and Starting Position
Set the seat height so that when you grab those handles, your elbows should be about at chest level. Grab them with hands roughly shoulder width apart, palms turned inward, keeping wrists straight instead of bent to avoid putting extra stress on joints. Feet need to stay planted flat on the ground while doing this exercise. Core muscles should be engaged throughout, and make sure the upper part of the back is pressed against the bench for proper support. According to some recent studies published last year in a fitness journal called Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, people who don't adjust their hand placement correctly end up straining their shoulders about 22 percent more during these kinds of exercises.
Optimizing Range of Motion for Full Pectoral Contraction
Squeeze the handles together until they nearly touch, holding the contraction for 1–2 seconds. Return slowly, stopping when elbows reach shoulder level to avoid overstretching connective tissues. This 30–40° range optimizes pectoral engagement while minimizing anterior deltoid involvement.
The Importance of Scapular Retraction and Controlled Movement
Retract your shoulder blades before each repetition to stabilize the shoulder girdle and create a solid base for pectoral force generation. Avoid letting shoulders roll forward during the eccentric phase—a common error linked to 34% of rotator cuff injuries in resistance training (American Council on Exercise, 2022).
Avoiding Momentum: Why Muscle Control Beats Speed
Using momentum shifts effort from the chest to the front delts and triceps. Focus on a 3-second concentric phase and a 4-second eccentric phase. Studies show tempo-controlled reps produce 20% greater pectoralis major activation than ballistic movements. If you feel the need to jerk the handles, reduce resistance by 10–15%.
Correcting Postural Errors That Reduce Safety and Effectiveness
Why Arching the Back Compromises Spine Safety and Muscle Focus
Excessive lower back arching shifts stress from the chest to the lumbar spine, increasing injury risk by 12–19% during chest-focused movements (Biomechanics Research 2023). This misalignment also reduces pectoral activation by up to 30%, as upper traps and shoulders compensate. To maintain spinal safety and muscle focus:
- Keep feet flat and knees bent at 90° to limit pelvic tilt
- Engage your core before initiating movement
- Visualize “pulling the ribs down” to prevent hyperextension
Maintaining a Neutral Spine Throughout the Fly Motion
A neutral spine—ears over shoulders, shoulders over hips—ensures efficient force transfer through the chest. Research shows this posture improves pectoralis major activation by 17% compared to flexed or overarched positions. For consistent form:
- Adjust seat height so handles align with mid-chest
- Squeeze shoulder blades together before gripping handles
- Exhale during the concentric phase to reinforce core engagement
Using Leg Stability Without Allowing Lower Body Compensation
While leg drive aids stability, excessive movement reduces chest isolation. A 2023 EMG analysis found that >2 inches of hip shift decreases pectoral activation by 24%. To balance stability and isolation:
- Press heels firmly into the floor without lifting toes
- Maintain a constant knee angle throughout
- Choose a weight that allows controlled 3-second eccentric phases
Enhancing Chest Isolation and Mind-Muscle Connection
Preventing Shoulder Dominance During Butterfly Machine Reps
Despite its chest-focused design, improper execution causes anterior deltoid dominance in 53% of novice users (Strength & Conditioning Journal 2023). Keep shoulder blades retracted throughout the movement to prevent forward rolling. Reducing grip width by 10–15% can increase pectoral engagement by 22% while limiting deltoid interference.
Developing Mind-Muscle Connection for Maximum Pectoral Activation
Intentional focus boosts pectoral EMG activity by 19% compared to passive repetitions. Enhance neuromuscular signaling by:
- Initiating each rep with 2 seconds of pre-contraction
- Performing partial-range "pulse" reps at peak squeeze
- Visualizing bringing elbows toward the sternum, not just pushing handles forward
Adjusting Seat Height and Pad Position for Ideal Alignment
Set the backpad to align with your scapular midpoint—78% of users under 5'10" require adjustments below factory presets. Pad distance should allow a 15–20° elbow bend when hands meet, maintaining constant tension on the pectoralis major.
Is Complete Chest Isolation Possible? Addressing the Debate
No exercise achieves 100% isolation, but the Butterfly Machine delivers 83% pectoral activation efficiency when properly set—outperforming dumbbell flies (62%) and cable crossovers (71%). Prioritize tempo-controlled reps (3 seconds concentric, 2 seconds eccentric) over heavy loading to maximize isolation.
Ensuring Safety, Longevity, and Machine Performance
Essential Warm-Up Routines Before Using the Butterfly Machine
Begin every session with 5–8 minutes of dynamic stretching for the chest, shoulders, and rotator cuffs. Light resistance band pull-aparts or push-ups prime the pectoralis major and improve joint mobility. Targeted warm-ups reduce injury risk by 34% compared to static stretching alone (Sports Medicine Review 2023).
Choosing the Right Weight: Balancing Intensity and Control
Select a weight that allows 8–12 controlled reps with proper form. If elbows flare or shoulders hike, reduce resistance by 10–15%. Overloading leads to compensatory recruitment, undermining chest activation.
Recognizing Signs of Overexertion or Incorrect Setup
Persistent joint pain, uneven soreness, or audible cable grinding signal incorrect use. Adjust seat height if elbows fall below shoulder level. Improper pad alignment increases sternoclavicular joint stress by 27% (Proper Machine Alignment).
Basic Maintenance: Lubrication, Cable Alignment, and Joint Checks
Perform monthly inspections: lubricate pivot points with silicone-based spray, check cables for symmetrical tension, and tighten loose bolts on handles and seat brackets. Facilities using preventative maintenance report 41% fewer malfunctions over 12 months (Equipment Maintenance Strategies, Industrial Fitness Journal 2023).
FAQs about the Butterfly Machine
What muscles does the butterfly machine target?
The butterfly machine primarily targets the chest muscles, specifically the pectoralis major and minor, while minimizing shoulder and triceps involvement.
How should I adjust the seat on a butterfly machine?
The seat should be adjusted so that your elbows are at chest level when you grab the handles, ensuring proper alignment and muscle engagement.
Why is scapular retraction important on a butterfly machine?
Scapular retraction stabilizes the shoulder girdle, creating a solid foundation for chest activation and minimizing the risk of injury.
What are common mistakes to avoid when using the butterfly machine?
Avoid arching your back excessively, using momentum instead of controlled movements, and not maintaining proper shoulder alignment during the exercise.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Butterfly Machine: Design and Primary Function
- Mastering Proper Form and Technique on the Butterfly Machine
- Correcting Postural Errors That Reduce Safety and Effectiveness
- Enhancing Chest Isolation and Mind-Muscle Connection
- Ensuring Safety, Longevity, and Machine Performance
- FAQs about the Butterfly Machine

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 ID
ID
 UK
UK
 ET
ET
 GL
GL
 HU
HU
 MT
MT
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 GA
GA
 HY
HY
 AZ
AZ
 KA
KA
 UR
UR
 BN
BN
 LA
LA
 UZ
UZ
 KU
KU
 KY
KY
